Statics Continued
Prof. Martha Selby
03-01-2014
Prepared by: Walter Bennette
Statics
Statics
The study of rigid bodies that are in equilibrium
Free Body Diagrams
A free body diagram is a sketch of the body and all the forces acting on it.
3 Steps in drawing a free body diagram
- Isolate the body, remove all supports and connectors.
- Identify all external forces acting on the body.
- Make a sketch of the body, showing all forces acting on it.
Is this you? Don't worry

Free Body Diagrams
Body in equilibrium
3 Steps in drawing a free body diagram
- Isolate the body, remove all supports and connectors.
- Identify all external forces acting on the body.
- Make a sketch of the body, showing all forces acting on it.
Free Body Diagrams
Body in equilibrium

Free Body Diagram
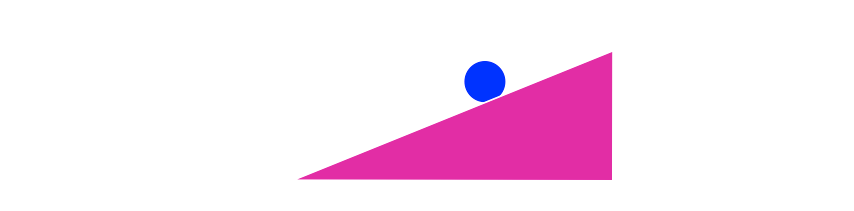
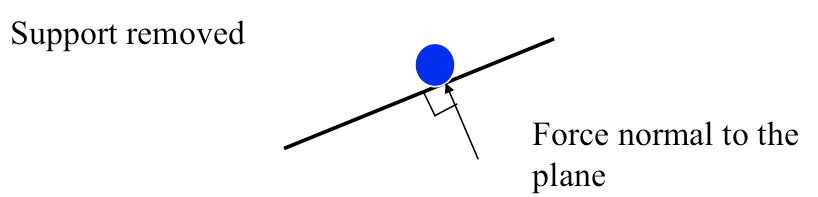
Inclined Plane (no friction)
Cable, Rope, or Chain
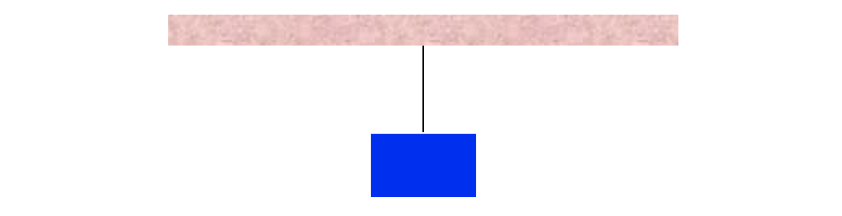
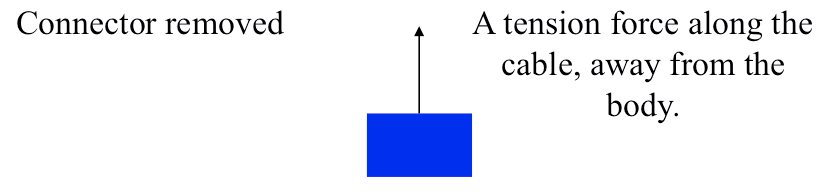
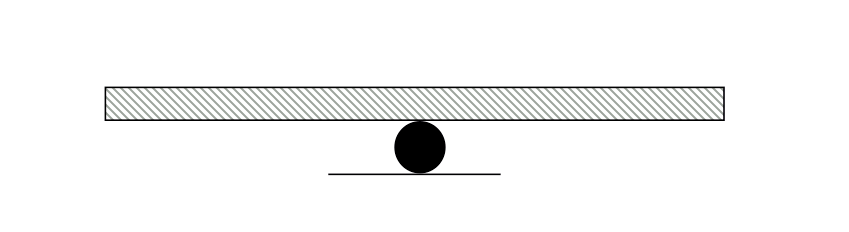
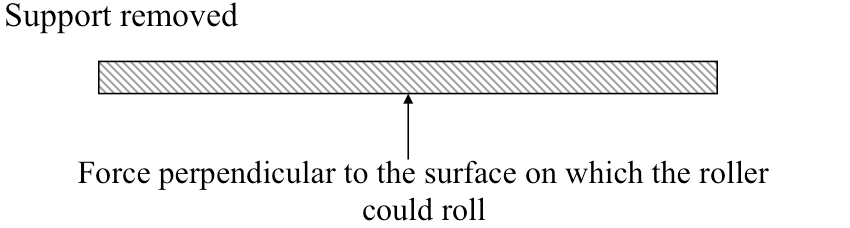
Roller or simple support
Pin or hinge

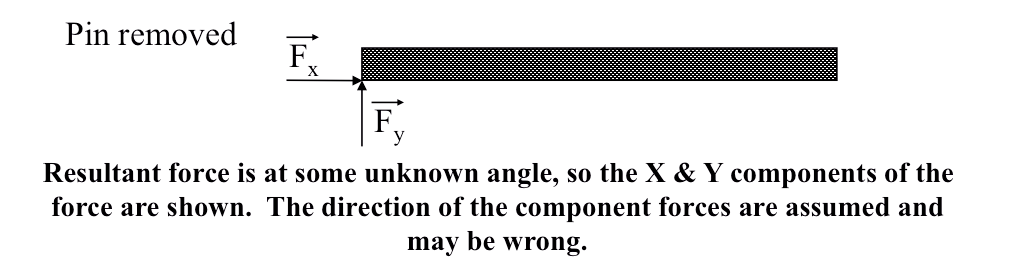
Equilibrium
A body is in equilibrium if the sum of all the external forces and moments acting on the body are zero.
1) \( \sum F_x = 0 \)
2) \( \sum F_y = 0 \)
3) \( \sum M = 0 \ (about \ any \ point) \)
Steps in solving a statics problem
- Draw a free body diagram.
- Choose a reference frame. Orient the X & Y axes.
- (most often X is chosen in the horizontal direction and Y is chosen in the verical direction)
- (most often X is chosen in the horizontal direction and Y is chosen in the verical direction)
- Choose a convenient point to calculate moments around.
- (most often this will be at the pin connection)
- (most often this will be at the pin connection)
- Apply the 3 equilibrium equations and solve for unknowns.
Example
Problem
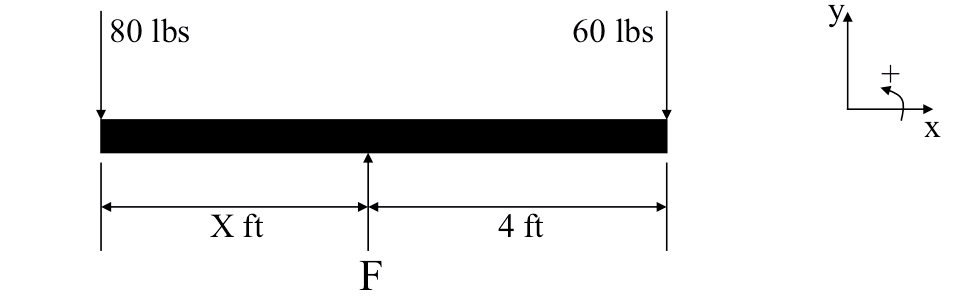
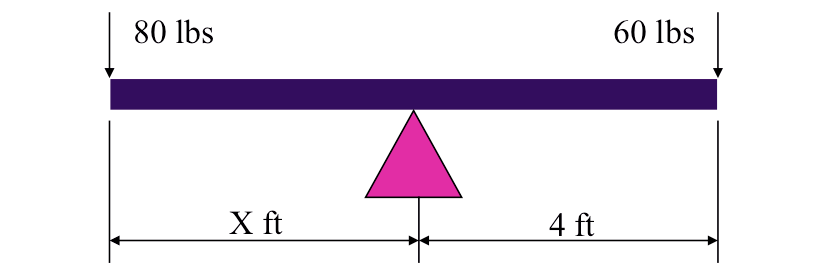
Two children balance a see saw in horizontal equilibrium. One weights 80 pounds, and the other weighs 60 pounds and is sitting 4 ft from the fulcrum. Find the force the fulcrum applies to the beam and the distance from the fulcrum to the 80 lb child. (Neglect the mass of the see-saw.)
Diagram
Steps in solving a statics problem
- Draw a free body diagram.
- Choose a reference frame. Orient the X & Y axes.
- (most often X is chosen in the horizontal direction and Y is chosen in the verical direction)
- (most often X is chosen in the horizontal direction and Y is chosen in the verical direction)
- Choose a convenient point to calculate moments around.
- (most often this will be at the pin connection)
- (most often this will be at the pin connection)
- Apply the 3 equilibrium equations and solve for unknowns.
Example
Free Body Diagram

Solution
\( \sum F_x = 0 = No \ X \ forces \).
\( \sum F_y = 0 = -80 + -60 + F \ \ \longrightarrow \ \ F=140 \ lbs \)
\( \sum M_{fulcrum}=0=80*X -60*4 \ \ \longrightarrow \ \ X=3 \ ft \)
Homework
Due March 12th (not this Wednesday, but next)
- 12.27, 12.30, 12.34, 12.36
(We will cover more statics this Wednesday)
In class problem
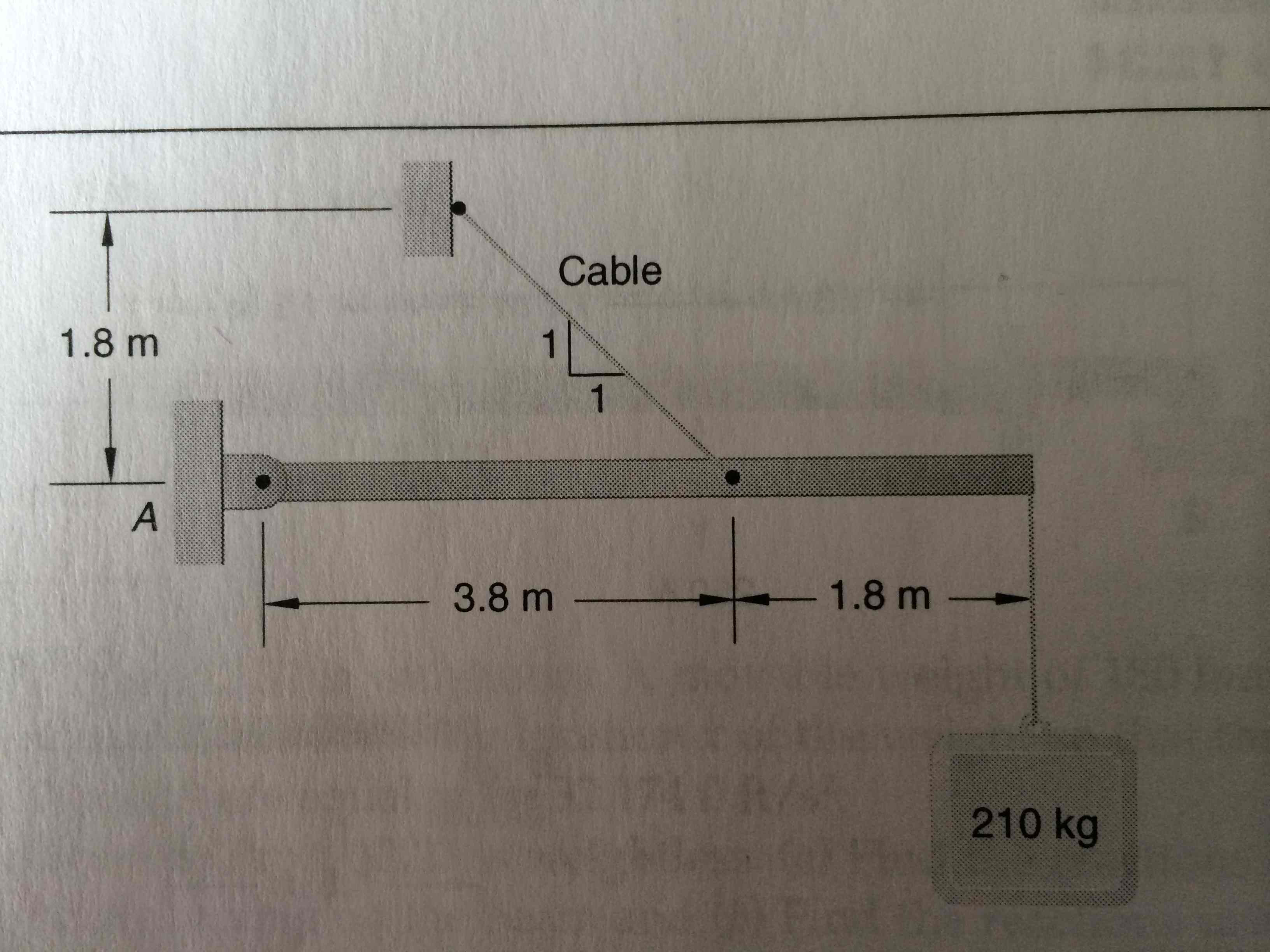
The uniform beam shown above has a mass of 180kg. Determine the resultant pin reaction at A and the tension in the cable.